- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
Can CBD Oil treat Alzheimer’s & Dementia
Cannabis has been used over the centuries to treat many conditions including inflammation, gut conditions and now also on the list Alzheimer’s Disease which is the most common neurological condition in the UK.
“Research conducted shows that, in 2019, there were over 850,000 people with dementia in the UK (Alzheimer’s Society, 2019).”
In this new world of cannabis therapy the plant has been under intensive studies since the beginning of the 2000’s because of the known effects on the endocannabinoidiome system with studies and research now being carried out at Johns Hopkins University’s Center for Psychedelic and Consciousness Research.
CBD Oil for Alzheimer’s ?
How can the (ECS) endocannabinoid system be a driver in the development for treatments of Alzheimer’s Disease, and how can (CBD) cannabidiol and other cannabinoids help with the treatment of the disease, the following points have been found out through various white papers, but stay with us on these points as they are quite technical.
- Amyloid plaques (aggregates of abnormally configured proteins) in the body are linked to Alzheimer’s Disease and cognitive decline are reduced by the further integration of CB2 receptors found in CBD oil reducing the build up of Amyloid plaques which in turn reduce the rate of cognitive decline
- Given the effects of cannabinoids on the endocannabinoid system (ECS) the cannabinoids may be good candidates for treating Alzheimer’s Disease because of they’re modulatory nature.
- New clinical trials have already reported that cannabinoids might be useful for reducing some symptoms of Alzheimer’s & Dementia in patients and further analysis has revealed changes in the brain due to the CB2 receptors increasing in the frontal or parahippocampal cortex, “probably in a time-dependent manner.” while the expression of CB1 cannabinoid receptors is decreased.
- The enzymes or FAAH (Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase) and MAGL (monoacylglycerol lipase) which metabolize the endocannabinoids anandamide and 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) , respectively, increases in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients.
- Increased expression of CB2 receptors is pronounced in and around amyloid plaques (aggregates of abnormally configured proteins that are considered a hallmark of Alzheimer’s Disease and cognitive decline), indicating a correlation between the ECS and plaque deposition.
- There is also a third enzyme DAGL (diacylglycerol lipase) that synthesises with 2-AG this also increases the cognitive brain ability of those with Alzheimer’s.
Those with Alzheimer’s may be put of by the effects of THC which can be considered as a contaminant for patients looking for effective medical qualities but the CBD part that fires the receptors 2-AG which in turn lowers the amyloid plaques and improves cognitive brain function.
To read the research and findings from the full paper please follow this link Understanding the Modulatory Effects of Cannabidiol on Alzheimer’s Disease.
Alzheimer’s and the Gut
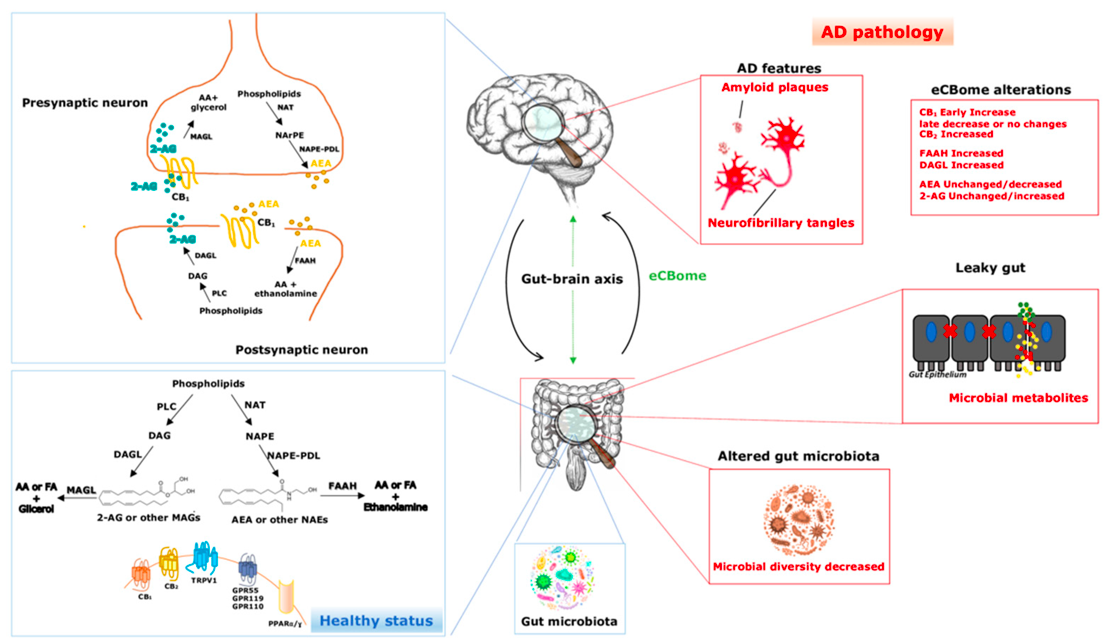
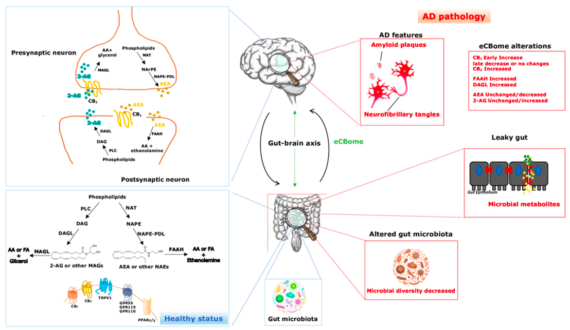
The gut microbiome has been at the forefront of new medical research including that we now know that the gut has interactions with the endocannabinoid system that can effect and trigger disease like cancer, Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s and obesity.
The ECS (endocannabinoid system) has a direct bridge between the gut bacteria and the brain with mood and every other type of function by passing signals back and forth in a kind of relationship as shown below.
The recent study “The Endocannabinoid System: A Bridge between Alzheimer’s Disease and Gut Microbiota” digs in deeper to the relationship with the endocannabinoid (ECB) system the gut microbiome are increasingly emerging as important players in maintaining the general homeostasis and the health status of the host.
Further to this the ECS may be key to mediating the connection between gut flora dysbiosis and Alzheimer’s physiopathology and these systems must be in sync otherwise they could be directly correlated to many types of disease
To read more of this research A Bridge between Alzheimer’s Disease and Gut Microbiota
Treating Dementia with CBD and targeting CBD2







You must log in to post a comment.